
Which Foods Causes Acne
Acne is one of the most common skin conditions globally in young adults, affecting millions of people from adolescence through adulthood. While most associate it with hormonal changes during puberty, there's growing evidence that diet plays a significant role in exacerbating or alleviating this skin issue and teenage acne in young adults.
This blog post delves into the intricate relationship between what we eat and acne in young adults, providing a comprehensive look at which foods may cause acne and how you can modify your diet to achieve clearer skin and less acne itself.
Understanding the dietary triggers of acne not only helps in managing the condition but also contributes to overall skin health. As we explore more research this topic, we'll uncover various foods linked to acne, backed by scientific studies and expert opinions developing acne themselves.
By the end of this post, you'll have more research and a clearer understanding of how to tailor your diet to potentially avoid foods that reduce acne flare-ups and maintain healthier skin.
Understanding Acne and Its Causes
What is Acne?
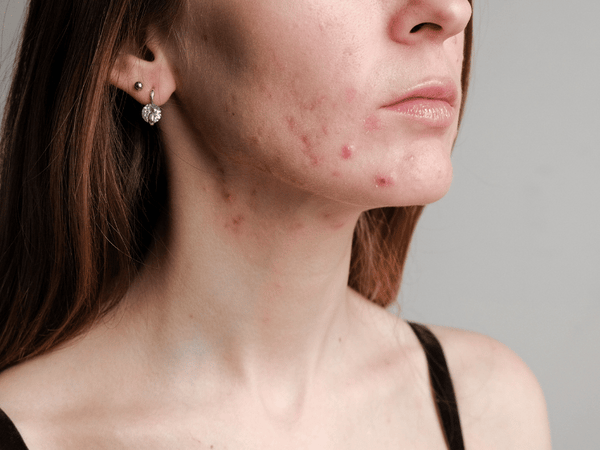
Acne is a skin condition characterized by the appearance of pimples, blackheads, and cysts. It primarily affects areas of the skin with a higher number of oil glands, including the face, back, and chest. There are several types of acne, which include:
-
Comedonal acne: This type appears mostly as blackheads and whiteheads and is caused by blocked hair follicles.
-
Inflammatory acne: This results from infections within the blocked follicles, leading to red, inflamed pimples.
-
Cystic acne: is the most severe form, characterized by large, painful cysts beneath the skin.
Each type of acne can have a different trigger and may respond differently to treatment.
General Causes of Acne
As a result of bacteria, oil, or dead skin cells clogging your pores, acne develops.
Here are the key factors contributing to the development of acne:
-
Oil production: Overactive sebaceous glands can produce excess oil that clogs pores.
-
Dead skin cells: These can accumulate and plug follicles, leading to pimples.
-
Bacteria: The presence of bacteria can inflame blocked pores and worsen acne.
Hormonal changes, particularly during puberty, pregnancy, and with certain medical conditions, can make acne worse, as acne lesions can significantly increase oil production, exacerbating acne.
Myths vs. Facts About Acne Causes
There are many misconceptions about what causes acne. Here are some debunked myths developing acne and the truths behind them:
-
Myth: Only teenagers get acne.
-
Fact: Acne can affect anyone at any age, though it is more common in teenagers due to hormonal changes.
-
Myth: Acne is caused by dirty skin.
-
Fact: While surface dirt and oil can contribute to acne, the main causes are deeper within the skin and more related to internal factors like hormones and genetics.
-
Myth: Eating greasy food causes acne directly.
-
Fact: Greasy food has little direct effect on acne but a poor diet can affect overall skin health.
The Link Between Diet and Acne
Overview of How Diet Can Impact Acne
Recent research has increasingly supported the idea that diet can significantly impact acne, though the extent to which dairy intake and nature of diet affect this impact can vary from person to person. The main concept here revolves around the relationship between food, dairy intake, and inflammation levels in the body. Foods that promote inflammation can aggravate acne, while diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods might help to alleviate it.
-
Scientific Evidence: Studies have shown that high glycemic index foods and dairy can trigger acne in susceptible individuals. These foods cause a spike in insulin levels, which may increase oil production and worsen acne.
-
Inflammation: Chronic inflammation can damage skin cells and promote acne. Dietary choices that reduce inflammation may, therefore, improve skin health.
Nutrients and Acne
Certain nutrients have a direct effect on skin health, and adjusting your intake of these can help manage acne:
-
Vitamins and Minerals: Vitamins A, D, E, and zinc are particularly important for skin health. Vitamin A helps with the maintenance and repair of skin tissue, and a deficiency can lead to a worsened acne condition.
-
Antioxidants: These compounds fight free radicals, which can damage skin cells and contribute to acne. Fresh fruits rich in antioxidants include berries, green tea, and dark chocolate.
-
Omega Fatty Acids: Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish like salmon and sardines, can reduce inflammation and are linked to improved skin health.
By understanding more research how these nutrients affect the body and immune system, individuals developing acne can make more informed choices about their diets to potentially reduce acne symptoms.
Specific Foods That Can Cause Acne
Let’s delve into some more research on specific food groups and the worst foods known to potentially trigger acne:
High-Glycemic Index Foods
Foods with refined carbohydrates and foods with a high glycemic index (GI) cause your blood sugar to spike rapidly. This spike leads to an increase in insulin resistance and can increase excess sebum- production and too much iodine, which can exacerbate acne by increasing oil production and inflammatory responses. the oily substance produced by sebaceous glands that can clog pores and cause acne.
Common high-GI Foods:
-
White bread
-
Sugary cereals
-
Pastries and sweets
-
Processed snacks
Dairy Products and Acne
Dairy and dairy products themselves, and therefore dairy products and dairy consumption, especially cow's milk and dairy milk and dairy consumption by itself, have been linked to acne in numerous studies. The theory is that cow's milk contains hormones that can mimic human hormones, thus potentially affecting oil production and leading to acne.
Types of Dairy Linked to Acne:
-
Skim milk (more so than whole milk, surprisingly)
-
Cheese
-
Yogurt
Fatty and Oily Foods
While the old belief that greasy food directly causes acne is a myth, diets of refined foods high in carbohydrates, processed sugary foods and foods high in unhealthy fats can influence inflammation and thus worsen existing acne and conditions.
Healthy vs. Unhealthy Fats:
-
Unhealthy: Fried foods, fast food
-
Healthy: Avocados, nuts, and seeds
Foods Rich in Hormones
Certain foods high in milk consumption dairy products, processed meats, and other animal products, due to the hormones given to animals, can have higher levels of hormones that might influence acne.
- Examples:
-
Certain types of beef
-
Some dairy products
Other Diet-Related Factors Affecting Acne
The Role of Food Allergies
Food allergies and sensitivities can play a significant role in skin health, including the occurrence of acne. An allergic reaction to eating foods can cause inflammation that can worsen acne and may manifest as skin irritation or acne.
Identifying Food Allergies:
-
Common allergens include dairy, nuts, soy, and gluten.
-
Symptoms might include hives, itching, or gastrointestinal distress, along with acne flare-ups.
-
It's advisable to consult a healthcare provider for allergy testing if you suspect a link between your diet and skin condition.
The Impact of Stress Eating
Stress eating can worsen acne due to the frequent consumption of high-glycemic, fatty, and processed foods, and refined carbohydrates, which might exacerbate acne. The two studies suggest that hormonal changes associated with stress also contribute to acne development.
Managing Stress and Diet:
-
Incorporate stress management techniques such as meditation, exercise, and adequate sleep into your routine.
-
Choose foods that are known to combat stress and inflammation, such as leafy greens, berries, and foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
Importance of a Balanced Diet
Maintaining a balanced diet is crucial for overall health and can significantly impact hormone levels that influence skin health, including acne itself. A diet lacking in certain nutrients processed foods can lead to deficiencies in hormone levels that may exacerbate acne.
Components of a Balanced Diet for Skin Health:
-
A rich variety of fruits and vegetables is needed to ensure a good intake of vitamins and antioxidants.
-
Adequate protein sources, both animal and plant-based, are needed to support skin repair and health.
-
Healthy fats come from sources like fish, nuts, and seeds, which can help reduce inflammation.
How to Identify If Your Acne Is Food-Related
Determining whether your acne is related to your diet involves observing and experimenting with what you eat and noting the effects on your skin.
Keeping a Food and Acne Diary
A practical way to track potential food-related acne triggers is by keeping a diary:
How to Keep a Diary:
-
Record everything you eat and drink, along with the timing of acne flare-ups.
-
Note other factors that may affect your skin, such as stress levels and sleep quality.
Elimination Diet and Acne
An elimination diet can be a powerful tool in identifying certain foods, that trigger your acne:
Conducting an Elimination Diet:
-
Eliminate common triggers from your diet for a period of time, usually 4-6 weeks.
-
Gradually reintroduce these foods one at a time and observe any changes in your skin condition.
This approach can help pinpoint specific dietary causes of acne and enable you to make informed decisions about which foods to avoid.
How Koze LED Face Mask Can Help Manage Acne
The Koze LED Face Mask harnesses the power of LED light therapy, a non-invasive treatment that uses varying wavelengths of light to target different skin concerns, including acne. Light-emitting Emitting Diode (LED) therapy has been clinically proven to offer benefits for skin health, making it a popular choice among dermatologists and skincare enthusiasts.
The Science Behind LED Light Therapy for Acne
LED light therapy works by emitting specific colors of light that penetrate the skin at different depths. Each color wavelength provides unique benefits:
Blue Light: Targets and destroys acne-causing bacteria on the skin’s surface and in pores, helping to treat and prevent acne.
Red Light: Promotes healing and reduces inflammation, which can minimize the appearance of acne scars and improve skin texture.
Yellow Light: reduces hyperpigmenations, improves lymphatic drainage, and reduces puffiness.
Features of the Koze LED Face Mask
The Koze LED Face Mask combines both red and blue light settings in one device, providing a dual-action approach to managing acne:
-
Adjustable Settings: Users can choose between blue, red, or a combination of both lights, depending on their specific skin needs.
-
Safety and Comfort: Designed with non-UV emitting lights, the mask is safe for regular use and is built to comfortably fit the contours of the face.
-
Ease of Use: The mask is user-friendly, designed for at-home use with sessions typically lasting between 10 to 20 minutes.
Benefits of Using the Koze LED Face Mask for Acne Management
Using the Koze LED Face Mask as part of your skincare routine can provide multiple benefits:
-
Effective Acne Treatment: Regular use of the mask can significantly reduce active acne breakouts and prevent new ones from forming.
-
Reduction in Inflammation: The red light setting reduces skin inflammation and can accelerate healing, helping to clear up the complexion.
-
Improvement in Skin Texture: Over time, light therapy can help smooth out the skin and reduce the appearance of scars, giving a healthier and more even complexion.
-
Convenience and Cost-Effectiveness: Provides an at-home treatment option that can reduce the need for expensive clinical treatments.
How to Incorporate the Koze LED Face Mask into Your Routine
To achieve the best results, incorporate the mask into your daily skincare regimen:
1. Cleanse the Skin: Start with a clean face. Remove all makeup and debris to ensure the light can penetrate effectively.
2. Use the Mask: Wear the mask according to the recommended time from the manufacturer. You can use it daily or as advised by a skincare professional.
3. Follow Up Care: After using the mask, apply skincare products that target your specific concerns, such as moisturizers or spot treatments.
Treatment and Prevention of Acne
Acne can be a persistent condition, but with the right strategies, it can be managed effectively. Below, we delve into various treatment options and preventive measures to help maintain clearer skin.
Dietary Changes for Clearer Skin
One of the first steps in treating and preventing acne is to consider dietary adjustments. As discussed earlier, certain foods can exacerbate acne, while others might help alleviate it.
Foods to Avoid:
-
High glycemic index foods such as sugary snacks and white bread
-
Dairy products, particularly skim milk
-
Foods rich in unhealthy fats like fast food
Foods to Include:
-
Low glycemic diet index foods like whole grains and leafy greens
-
Antioxidant-rich foods such as berries and nuts
-
Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish like salmon and flaxseeds
Implementing these dietary changes can help reduce inflammation and improve hormone regulation, both of which studies suggest are beneficial in managing acne.
Skincare Routines to Complement Dietary Changes
In addition to dietary changes, establishing a consistent skincare routine can significantly impact acne treatment.
-
Cleansing: Use a gentle cleanser twice a day to remove impurities and excess oil.
-
Exfoliating: Incorporate mild exfoliation a few times a week to clear dead skin cells that can clog pores.
-
Moisturizing: Even oily skin needs hydration; opt for oil-free, non-comedogenic moisturizers.
-
Spot Treatments: Products containing benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or sulfur can help treat existing breakouts.
Advanced Treatments
For more stubborn cases of acne, consider the following advanced treatment options:
-
Topical Retinoids: Help clear acne by unclogging pores and reducing oiliness.
-
Antibiotics: Can be used to reduce bacteria and inflammation for moderate to severe acne.
-
Hormonal Treatments: Such as birth control pills, which can help regulate hormones that trigger acne.
-
LED Light Therapy: As with the Koze LED Face Mask, this therapy uses blue and red light to reduce bacteria and inflammation.
Preventive Measures
Preventing acne involves more than just treating existing acne breakouts; it includes lifestyle adjustments to reduce the likelihood of acne reoccurring.
-
Stress Management: Stress can trigger and worsen acne, so incorporating stress-reduction techniques like yoga, meditation, and sufficient sleep is crucial.
-
Regular Exercise: Helps reduce stress and promotes healthy blood circulation, which can improve skin health.
-
Adequate Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps to detoxify your body and keep your skin hydrated.
When to See a Dermatologist
While home treatments can be effective, it’s important to consult a dermatologist if:
-
Acne persists despite home treatments.
-
Acne is severe and painful.
-
Acne significantly affects your quality of life.
A dermatologist can provide customized treatments and monitor your progress, ensuring the most effective care tailored to your skin's needs.
Conclusion
The relationship between diet and acne is complex and multifaceted, yet understanding this connection can be a powerful tool in managing and potentially reducing acne outbreaks. This blog post has explored various foods and dietary habits that can trigger acne outbreaks, highlighted the importance of balanced nutrition, and provided practical advice on identifying food-related acne triggers through observation and elimination diets.
While dietary adjustments can play a crucial role in skin health, they are just one aspect of a comprehensive acne management strategy. Incorporating treatments like the Koze LED Face Mask can enhance your efforts, offering a safe and effective way to combat acne directly from the comfort of your home. This innovative technology, combined with dietary awareness and proper skincare routines, can lead to significant improvements in your skin’s appearance and health.
Ultimately, managing acne effectively requires a holistic approach that considers diet, skincare practices, and sometimes professional advice. We encourage our readers to experiment with these recommendations while consulting with healthcare professionals to tailor a plan that best suits their individual needs.
As we continue to explore the intersections of diet, technology, and skincare, we invite you to share your experiences and insights. Have you noticed changes in your acne based on dietary choices? Have you tried LED light therapy for acne management? Your stories can help others in their journey toward clearer skin.



