Light therapy for psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic, non-contagious skin condition that affects people worldwide and is characterized by red, flaky patches of skin covered with silvery scales. The emotional and physical impact of psoriasis can be substantial, leading many to seek effective treatments to manage their symptoms. Among the various treatments available, UV (ultraviolet) light therapy stands out for its ability to significantly reduce the signs and symptoms of psoriasis for many patients.
This comprehensive guide will explore everything you need to know about psoriasis UV treatment, including its benefits, the treatment process, potential side effects, and how it compares to alternative topical therapies like red light therapy. Our goal is to provide you with deep, useful knowledge on this topic, including lists, facts, tables, and even case studies, to ensure you have all the information you need to understand this valuable psoriasis treatment and option.
Understanding Psoriasis
Psoriasis is more than just a skin condition; it's a complex autoimmune disease that can have far-reaching effects on an individual's health and well-being. In this section, we'll delve into the definition of psoriasis, its symptoms, common triggers, risk factors, and the impact it has on quality of life.
Definition and Symptoms
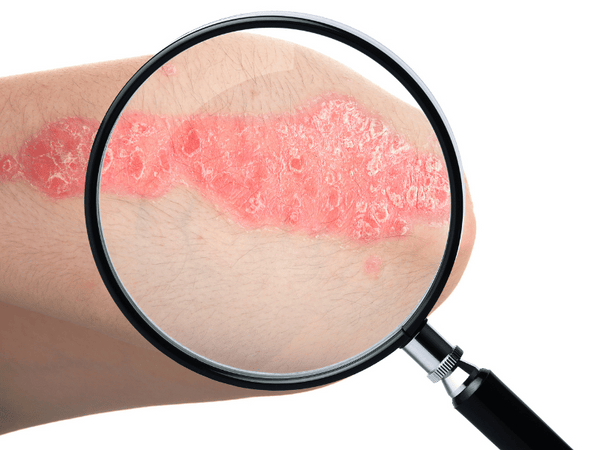

At its core, plaque psoriasis is characterized by an accelerated skin cell production process. In a healthy individual, skin cells are typically replaced every 28 to 30 days. However, in people with severe psoriasis, this process is significantly faster, occurring in just 3 to 4 days. This rapid turnover during early skin aging leads to the buildup of skin cells on the surface, resulting in the telltale patches known as plaques. These plaques can be itchy, painful, and can crack and bleed in severe cases.
The most common symptoms of psoriasis include:
-
Red patches of skin covered with thick, silvery scales
-
Dry, cracked skin that may bleed
-
Itching, burning, or soreness
-
Thickened, pitted, or ridged nails
-
Swollen and stiff joints (in cases of psoriatic arthritis)
Common Triggers and Risk Factors

Psoriasis can be triggered or exacerbated by various factors, including:
-
Stress: High stress levels can trigger flare-ups.
-
Injury to the skin: Cuts, scrapes, or sunburns can prompt the development of psoriasis plaques.
-
Infections: Certain infections, especially strep throat, can lead to psoriasis in some individuals.
-
Medications: Certain medications, including beta-blockers and lithium, can worsen psoriasis symptoms.
-
Weather: Cold, dry weather can trigger psoriasis flare-ups, while warm, sunny climates may improve symptoms.
Risk factors for developing psoriasis include:
-
Family history: Having a family member with psoriasis increases your risk.
-
Viral and bacterial infections: People diagnosed with HIV and children with recurrent infections like strep throat are more likely to develop psoriasis.
-
Obesity: Excess weight increases the risk and severity of psoriasis.
-
Smoking: Smoking tobacco not only increases the risk of psoriasis but can also exacerbate the severity of the condition.
Impact on Quality of Life
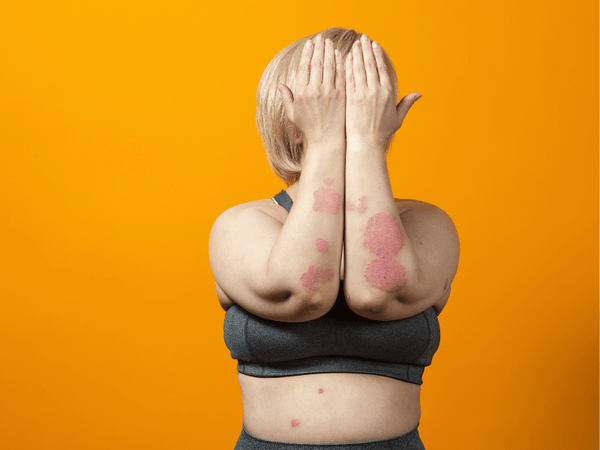

Psoriasis can have a profound impact on an individual's quality of life. The visibility of the condition can lead to social stigma, emotional distress, and a lack of self-confidence. In addition, the constant itch and discomfort can disrupt sleep and daily activities. Moreover, psoriasis is often associated with other serious health conditions, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and depression, further affecting an individual's overall well-being.
Understanding the complexities of psoriasis is crucial to managing the condition effectively. By recognizing the symptoms, triggers, and risk factors, individuals can work with healthcare professionals to develop a comprehensive treatment plan that addresses both the physical and emotional aspects of the disease.
Overview of UV Treatment for Psoriasis
Ultraviolet (UV) light therapy, also known as phototherapy, is a widely used treatment for managing psoriasis. It involves exposing the skin to controlled amounts of natural or artificial UV light under medical supervision. In this section, we'll explore the types of UV treatments, their mechanisms of action, and their efficacy in treating psoriasis.
Types of UV Treatment

There are two main types of UV light therapy used for psoriasis:
1. UVB Phototherapy: This therapy uses a specific wavelength of ultraviolet light (UVB) to target psoriasis lesions and plaques. UVB phototherapy treatments can be administered in two forms:
-
Narrowband UVB: This is the most common form of phototherapy and uses a narrow range of UVB light wavelengths. It is considered more effective and safer than broadband UVB.
-
Broadband UVB: This older form of phototherapy uses a broader range of UVB wavelengths but is less commonly used today due to the higher efficacy and safety profile of narrowband UVB.
2. PUVA (Psoralen + UVA light) Therapy: This first treatment of psoriasis combines a medication called psoralen with exposure to UVA light. Psoralen makes the skin more sensitive to UVA light, enhancing the treatment's effectiveness. PUVA is generally used for more severe cases of psoriasis.
Mechanism of Action
UV light therapy works by slowing down the rapid growth of skin cancer cells and reducing the skin cancer inflammation itself, which are key characteristics of the skin cancer psoriasis treatment. The exact mechanism is not fully understood, but it is believed that UV light induces DNA damage in the skin cancer cells, triggering apoptosis (cell death), which helps the immune cells clear the skin cancer psoriasis plaques.
Efficacy and Success Rates
The success rates for treatment of psoriasis with UV and photodynamic therapy can vary depending on several factors, including the severity of the psoriasis, the type of UV treatment used, and the individual's response to photodynamic therapy. Generally, UVB phototherapy for psoriasis has been found to be an effective treatment in about 70% of cases, with patients experiencing significant improvement or clearance of psoriasis plaques.
PUVA therapy has a higher efficacy rate, with about 85% of patients seeing significant improvement. However, it is associated with a higher risk of side effects, including an increased risk of skin cancer, which is why it is typically reserved for more severe cases or when other treatments have failed.
Benefits of UV Treatment for Psoriasis

UV treatment for plaque psoriasis offers a range of benefits, making it a popular choice for those seeking relief from this chronic skin condition. Here are some of the key advantages of undergoing UV light therapy to treat plaque psoriasis:
Reduction of Symptoms
One of the primary benefits of UV for the treatment of psoriasis is its ability to significantly lessen skin inflammation and reduce the symptoms of psoriasis. Patients often experience:
-
Decreased scaling and flaking: UV light helps to slow down the excessive production of skin cells, leading to less scaling and flaking of the skin.
-
Reduced redness and inflammation: The anti-inflammatory effects of UV light can help to soothe the redness and irritation associated with psoriasis plaques.
Alleviation of itching and discomfort: Many patients report a reduction in the itching and discomfort that often accompany their psoriasis treatment, leading to an improved quality of life.
Decrease in Flare-Ups
Regular UV treatment sessions can help to reduce psoriasis symptoms and prevent or reduce the frequency of psoriasis flare-ups. By keeping the symptoms under control, patients can enjoy longer periods of remission and fewer disruptions to their daily lives.
Improvement in Skin Appearance
UV treatment nail psoriasis can lead to a more even skin tone blue light, and a smoother texture for fair skin on darker skin tones, as the light therapy of ultraviolet rays helps to reduce the prominence of psoriasis plaques. This cosmetic benefit is particularly important for individuals who feel self-conscious about their darker skin's appearance.
Minimal Systemic Side Effects
Unlike some systemic medications used to treat psoriasis, UV treatment primarily targets the affected skin areas, minimizing the risk of side effects throughout the skin involved rest of the body. This makes it a safer option for long-term management of the condition.
Versatility and Convenience
UV treatment can be tailored to the individual needs of each patient, with adjustments made to the type of light, duration, and frequency of sessions. Additionally, advancements in technology have made it possible for some patients to undergo UV treatment at home with portable devices, adding a level of convenience to their treatment regimen.
Preparing for UV Treatment

Before starting UV treatment for psoriasis, it's essential to take certain steps to ensure the process is as effective and safe as possible. Here's what you need to know about preparing for your UV therapy sessions:
Consultation with a Dermatologist
-
Initial Assessment: Your dermatologist will evaluate your psoriasis to determine if UV treatment is a suitable option for you. This assessment may include reviewing your medical history, the severity of your condition, and any previous treatments you've tried.
-
Treatment Plan: If UV therapy is deemed appropriate, your dermatologist will develop a customized treatment plan, including the type of UV treatment, the frequency of sessions, and the duration of each session.
Understanding Treatment Protocols
-
Educational Materials: Your healthcare provider should provide you with information about the UV treatment process, potential side effects, and what to expect during and after your sessions.
-
Dosage Adjustments: The intensity and duration of UV exposure will be carefully adjusted based on your skin type, response to treatment, and any side effects you may experience.
Pre-Treatment Skin Care Tips
-
Avoid Sunburn: Prior to your treatment, it's crucial to protect your skin from sunburn, as sunburned skin can be more sensitive to UV light and increase the risk of side effects.
-
Moisturize: Keeping your skin well-moisturized can help improve the effectiveness of UV treatment and reduce discomfort during the sessions.
-
Medication Review: Inform your dermatologist about any medications you're taking, as some drugs can increase sensitivity to UV light and may need to be adjusted or temporarily stopped before treatment.
Preparing for Each Session
-
Wear Protective Clothing: For targeted UVB therapy, you'll need to wear clothing that exposes only the affected areas of your skin. For full-body treatments, you may be asked to wear special goggles to protect your eyes and genital shields for sensitive areas.
-
Remove Skincare Products: Before each session, remove any makeup, lotions, or other skincare products from the areas that will be exposed to UV light.
The UV Treatment Process
Understanding what to expect during the UV laser treatment and process can help alleviate any concerns and ensure a smooth experience. Here's a step-by-step guide to the typical UV therapy session for psoriasis:
What to Expect During Sessions
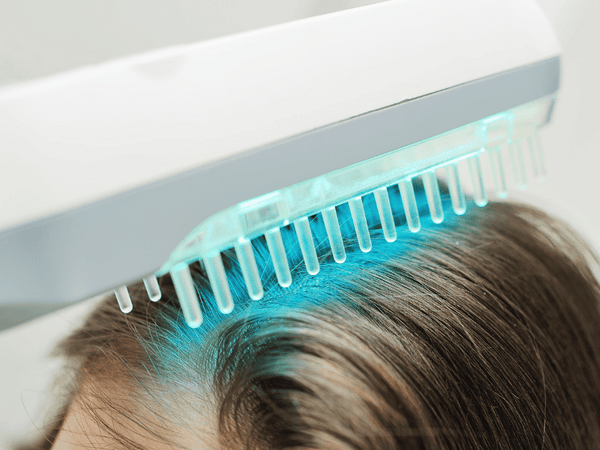

-
Arrival: Upon arriving at the clinic or hospital, you'll check in and be directed to the phototherapy treatment area.
-
Preparation: You'll change into appropriate attire, ensuring that the affected areas of your skin are exposed while protecting sensitive regions and your eyes with goggles or shields.
-
Exposure to UV Light: You'll stand or sit in a specially designed UV light booth or use a handheld device, depending on the type of treatment and the areas being treated. The UV light will be turned on for a predetermined amount of time, usually just a few minutes.
-
Monitoring: A healthcare professional will monitor your treatment to ensure that the UV exposure is within safe limits and adjust the intensity or duration as needed.
Duration and Frequency of Treatment
-
Initial Phase: Treatment typically starts with shorter exposure times, gradually increasing based on your skin's response and tolerance. This initial phase may involve sessions two to three times per week.
-
Maintenance Phase: Once your psoriasis shows improvement, the frequency of sessions may be reduced to once a week or less to maintain the benefits.
Safety Measures and Precautions
-
Eye Protection: It's crucial to wear protective goggles during the treatment to shield your eyes from harmful UV rays.
-
Skin Protection: Non-affected areas of your skin may be covered with clothing or sunscreen to minimize unnecessary exposure.
-
Follow-up Appointments: Regular appointments with your dermatologist are essential to monitor your progress, adjust treatment parameters, and manage any side effects.
After each session, you may notice a slight reddening of the treated skin, similar to a mild sunburn. This is generally normal and should subside within a day or two. It's important to follow your healthcare provider's instructions for post-treatment care, which may include applying moisturizers to soothe the skin.
Exploring Red Light Therapy for Psoriasis
In addition to traditional UV treatment, red and blue light therapy has emerged as a potential alternative for managing psoriasis symptoms. While it's a different approach from UV therapy, it offers some unique benefits worth considering. Here's what you need to know about red and blue light therapy for psoriasis:
Introduction to Red Light Therapy
Red light therapy, also known as low-level laser therapy (LLLT), is a laser treatment that involves exposing the skin to low levels of red or near-infrared light. Unlike UV light therapy, red light therapy does not have the same potential to cause skin damage, making it a safer option than ultraviolet radiation for some individuals.
Differences Between Red Light and UV Treatment
-
Wavelengths: Red light therapy uses wavelengths in the red to near-infrared spectrum (typically around 630–700 nm), which are different from the UV spectrum used in UVB and PUVA treatments.
-
Mechanism of Action: While UV treatment works by slowing down cell growth and reducing inflammation, red light therapy is believed to promote healing and reduce inflammation through different biological pathways.
-
Safety Profile: Red light therapy does not carry the same risks of skin aging and cancer associated with prolonged UV exposure.
Potential Benefits and Limitations
-
Benefits: Early studies suggest that red light therapy may help reduce the severity of psoriasis plaques, relieve inflammation, and promote skin healing. It's also non-invasive and generally well-tolerated by patients.
-
Limitations: More research is needed to fully understand the effectiveness of red light therapy for psoriasis, and it may not be as effective as UV treatment for more severe cases.
Research and Studies on Red Light Therapy for Psoriasis
Several studies have explored the use of red and blue light devices in therapy for psoriasis, with promising results. For example, a study published in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology found that red and blue light device therapy could significantly reduce the thickness and redness of psoriasis plaques. However, more large-scale and long-term studies are needed to establish its efficacy and optimal treatment protocols.
Potential Side Effects and Risks of UV Treatment
While UV treatment is generally safe and effective for managing psoriasis, it's important to be aware of the potential side effects and risks associated with this therapy. Here's what you need to know:
Short-Term Side Effects
-
Skin Redness: Similar to a mild sunburn, the treated skin may become red and tender after a session, usually subsiding within a few hours to a day.
-
Dryness and Itching: UV exposure can dry out the skin, leading to itching and discomfort.
-
Blisters or Burns: In rare cases, excessive UV exposure can cause blisters or burns, especially if the skin is not properly protected.
Long-Term Risks
-
Skin Aging: Prolonged UV exposure can lead to premature aging of the skin, including wrinkles, fine lines, and changes in texture.
-
Skin Cancer: There is an increased risk of skin cancer, particularly with long-term PUVA therapy. Regular skin checks with a dermatologist are essential for early detection.
-
Eye Damage: Without proper eye protection, UV treatment can increase the risk of cataracts and other eye conditions.
Managing Side Effects
-
Moisturize: Keeping your skin well-moisturized can help alleviate dryness and itching.
-
Sun Protection: Use sunscreen and protective clothing to shield your skin from natural sunlight, especially on days when you have UV treatment.
-
Follow Guidelines: Adhere to the recommended exposure times and frequencies to minimize the risk of side effects.
Aftercare and Maintenance
Proper aftercare and maintenance of healthy skin are crucial for maximizing the benefits of UV treatment for psoriasis and minimizing potential side effects. Here are some essential tips for taking care of your skin after your treatment sessions:
Post-Treatment Skin Care
-
Moisturize Regularly: Apply a gentle, fragrance-free moisturizer to keep your skin hydrated and reduce itching and flaking.
-
Avoid Harsh Skincare Products: Steer clear of products with strong fragrances, alcohol, or other irritants that can exacerbate skin sensitivity.
-
Cool Compresses: If you experience mild discomfort or redness after treatment, applying a cool, damp cloth to the affected areas can provide relief.
Monitoring for Changes in Symptoms
-
Keep Track of Your Progress: Take note of any improvements or changes in your psoriasis symptoms and share this information with your dermatologist during follow-up appointments.
-
Watch for Adverse Reactions: Report any unusual side effects or worsening of symptoms to your healthcare provider promptly.
Adjusting Treatment Plans
-
Follow-Up Visits: Regular check-ins with your dermatologist are essential for monitoring your response to treatment and making any necessary adjustments to your regimen.
-
Tailoring Treatment Frequency: Based on your progress, your dermatologist may alter the frequency of your UV sessions to maintain the benefits or reduce the risk of side effects.
Lifestyle Considerations
-
Sun Protection: Protect your skin from natural sunlight by wearing sunscreen and protective clothing, especially on treatment days and during peak sun hours.
-
Healthy Habits: Maintain a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management techniques to support overall skin health.
Alternative and Complementary Therapies
While UV treatment is a well-established option for managing psoriasis, many individuals also explore alternative and complementary therapies to complement their treatment plan. Here's an overview of some popular combination therapy options:
Topical Treatments
-
Corticosteroids: These are the most commonly prescribed medications for treating mild to moderate psoriasis and can help reduce inflammation and itching.
-
Vitamin D Analogues: Creams and ointments containing synthetic forms of vitamin D can slow skin cell growth.
-
Coal Tar: A traditional treatment for psoriasis, coal tar can reduce scaling, itching, and inflammation.
Systemic Medications
For more severe cases of psoriasis or those that are resistant to topical treatments, systemic medications may be prescribed:
-
Methotrexate: This medication can slow cell turnover and suppress inflammation.
-
Biologics: These are newer, injectable drugs that target specific parts of the immune system to treat psoriasis.
Lifestyle Changes and Natural Remedies
Incorporating healthy lifestyle habits and natural remedies can also support psoriasis management.
-
Diet: Some people find that certain dietary changes, such as reducing gluten or following an anti-inflammatory diet, can improve their symptoms.
-
Stress Management: Techniques like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing can help manage stress, which is a known trigger for psoriasis flare-ups.
-
Moisturizing: Regular use of moisturizers can help soothe and protect the skin, reducing dryness and scaling.
Phototherapy (Light Therapy)
In addition to UV treatment, other forms of light therapy, such as red light therapy, pulsed dye laser treatment, excimer laser, and targeted laser therapy, are being explored for their potential benefits in treating psoriasis.
It's important to note that the effectiveness of alternative and complementary therapies can vary from person to person. Always consult with your healthcare provider before trying new treatments to ensure they are safe and appropriate for your specific condition.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Psoriasis UV Treatment
How long does it take to see results from UV treatment?
Answer: The time it takes to see improvements can vary depending on the individual and the severity of their psoriasis. Some people may start noticing a reduction in symptoms within a few weeks, while others may require longer treatment periods.
Can UV treatment cure psoriasis?
Answer: While UV treatment can effectively treat and manage the symptoms of nail psoriasis and induce remission, it is not considered a cure for nail psoriasis. Ongoing treatment may be necessary to maintain the results.
Is UV treatment suitable for all types of psoriasis?
Answer: UV treatment is most commonly used for plaque psoriasis but can also be an effective treatment for other types of stable plaque psoriasis, such as guttate, inverse, and erythrodermic psoriasis. However, it may not be suitable for pustular psoriasis or certain other conditions.
How does red light therapy compare to UV treatment?
Answer: Red light therapy is a different approach that uses low-level red or near-infrared light. It's considered safer in terms of skin damage and less increased skin cancer risk or risk of increased risk of skin cancer than risk alone, but may not be as effective for severe psoriasis cases. It can be a complementary treatment to UV therapy for some individuals.
What are the long-term risks of UV treatment?
Answer: Long-term UV treatment, especially PUVA, can increase the risk of skin aging and the increased risk of skin cancer. Regular skin examinations and consultations with a dermatologist are essential to monitor for any adverse effects.
Can I continue using topical treatments while undergoing UV therapy?
Answer: In many skin cancer cases, you can use topical treatments in conjunction with UV therapy to develop skin cancer. However, it's important to consult with your dermatologist to ensure that the combination is safe and effective for your skin cancer-specific situation.
Conclusion
UV treatment offers a valuable option for managing psoriasis, providing relief from symptoms, and improving the quality of life for many individuals. By understanding the benefits, preparing properly, and following a tailored treatment plan, patients can maximize the effectiveness of this therapy. While it's important to be aware of the potential side effects and risks, with careful monitoring and a proactive approach, UV treatment can be a safe and effective part of your psoriasis management strategy. fewer treatments
Call to Action
If you're considering UV treatment for psoriasis or looking for ways to manage your condition by avoiding natural sunlight, we encourage you to:
-
Schedule a consultation: Talk to a dermatologist about whether UV treatment is right for you and discuss any concerns you may have.
-
Explore More Resources: Educate yourself about psoriasis and the various treatment options available to make informed decisions about your care.
-
Take Charge of Your Health: Be proactive in managing your psoriasis by following your treatment plan, adopting healthy lifestyle habits, and seeking support when needed.
Remember, you're not alone in your journey with psoriasis. With the right resources and support, you can take control of your symptoms and lead a fulfilling life.
Resources
For more information and support in managing plaque psoriasis, consider exploring the following resources:
1. The National Psoriasis Foundation is a leading organization dedicated to research, advocacy, and support for individuals with psoriasis. https://www.psoriasis.org/
2. The American Academy of Dermatology provides educational resources on psoriasis and helps locate dermatologists. https://www.aad.org/
3. The Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Alliance offers support and information for people affected by psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. https://www.papaa.org/
4. The British Association of Dermatologists offers patient information leaflets on psoriasis and its treatments. https://www.bad.org.uk/
5. Psoriasis Association: A UK-based charity dedicated to raising awareness and supporting those with psoriasis. https://www.psoriasis-association.org.uk/


